Introduction
Recently, the global prevalence of hypertension (HT) in both developed and developing countries was estimated to be 1.13 billion, with a prevalence of over 150 million in Europe [1,2]. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) comprises the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems. These components play an essential role in maintaining and regulating systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP), and heart rate (HR) [1]. An imbalance of ANS components can lead to cardiovascular disorders such as HT [2]. Therefore, the primary aim of controlling blood pressure (BP) in hypertensive patients is to balance the ANS. Recently, besides medication and lifestyle modification, breathing exercises (BE) have been a widespread practice for hypertensive patients [3–5].
The theorised mechanism of BE involved in ANS activation was revealed. Deep and slow breathing modulation via stimulation of the arterial baroreceptor leads to relatively decreased sympathetic activity and increased vagal tone, resulting in decreased BP and HR [6, 7]. BP reduction was also explained by increased parasympathetic tone in pursed lips and bee-humming breathing. Moreover, during prolonged expiration, lung tissue stretching and decreased dead space ventilation stimulate slow lung stretch receptors and increase parasympathetic system activation. In addition, humming sound creates vibration and acts like an auditory stimulus that might trigger the vagus nerve, and consequently, the parasympathetic tone increases [8, 9].
Based on the idea of the active cycle of breathing technique (ACBT), it is generally applied to people with chronic lung problems. The basic cycle comprises deep breathing, breathing control (BC), and huffing [10]. The developed BE consists of deep and slow, pursed-lip, and bee-humming. As each type of BE is involved in different mechanisms, we were interested in the combination effect of BE. Therefore, this study aims to compare the combination effect between the developed BE (1 – deep and slow with pursed-lip, 2 – deep and slow with bee-humming, 3 – pursed-lips with bee-humming, and 4 – deep and slow with pursed-lips with bee-humming) and deep and slow breathing on the haemodynamics and heart rate variability (HRV) parameters in hypertensive patients.
Subjects and methods
Study design
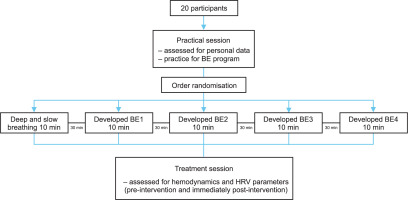
A repeated-measures design was conducted. The participants attended five BE sessions in a day. All interventions consisted of deep and slow breathing and 4 different breathing exercise cycles. The order of the intervention sessions was randomised. Participant recruitment started on 8th July and was completed on 24th Sep 2023. A previous study did not report the breathing patterns to have any adverse effects.
Patient population
Twenty participants were recruited from the Bangkok metropolitan region. Leaflet announcements were distributed on community boards at Chulalongkorn University and the Facebook social platform. Individuals were included if they were aged between 40 and 59 years old. Other inclusion criteria were essential hypertensive patients, both men and women, who receive anti-hypertensive medications. The participants also had to be willing to participate in the protocol. If the participants were unable to perform BE, they were excluded. Other exclusion criteria included smoking, secondary HT, chronic lung disease (chronic obstructive lung disease, asthma, or emphysema), and menopausal syndrome.
Measures
Haemodynamics assessment methods
The cardiovascular variables, including SBP, DBP, and HR, were assessed in a sitting position using an automatic blood pressure monitor (Yuwell YE670D). The cuff was placed on the upper level with the heart and the marker directly above the brachial artery. The data were recorded pre- and post-intervention of each BE session.
Heart rate variability (HRV) assessment methods
In this study, a Polar H10 (Polar Electro Oy, Kempele, Finland) heart rate monitor was used. The chest strap was secured on the participants’ chests, with the heart rate sensor positioned on the xiphoid process of the sternum. HRV measurements were obtained by detecting the heart’s electrical signals [11]. The Polar H10 transmitted data wirelessly via Bluetooth 4.0 to the HRV logger application, which then downloaded the information to an iPhone. Once the device connections were confirmed, the data collection process began by pressing the ‘record’ button. HRV parameters will be reported in the application. To assess HRV, data were recorded pre- and post-each BE session. The HRV logger application had previously shown validity and reliability in our preliminary study compared to the Elite HRV, which was validated as the gold standard. The validity and reliability of the HRV logger are moderate-to-excellent.
The main parameters are time-domain and frequency-domain. The time domain describes the variability between inter-beat intervals (IBI), which is the period of each heartbeat. Besides the R-R interval, the metrics of the time domain consist of the standard deviation of the IBI of normal sinus beats (SDNN), the root mean square of successive differences between normal heartbeats (RMSSD), and lower HRV during high physical activity, which reflects sympathetic overactivity and parasympathetic under-activity [11]. The frequency-domain is accessed using program analysis that separates HRV into components based on frequency range. The high-frequency (HF) band (0.15–0.40 Hz) represents parasympathetic activity. The low-frequency (LF) (0.04–0.15 Hz) mainly indicates sympathetic activity [11]. The ratio of LF to HF (LF/HF) was used to estimate the balance between sympathetic and parasympathetic activity [12].
Experimental protocol
The day before the experiment, the participants were instructed to ensure they had an adequate amount of sleep of at least 6 hours and to refrain from alcohol, caffeinated drinks, and spicy food for at least 6 hours before their appointment. They were also asked to take antihypertensive drugs as usual and to wear comfortable clothes on the day of the experiment.
Initially, the participants were instructed to complete a general characteristic and health status form. Subsequently, the participants were instructed in the study BE, and this practiced BE was accompanied by a video guide under the supervision of researchers until they could perform them correctly.
After 30 min of sitting quietly, an automatic sphygmomanometer measured the baseline haemodynamic parameters. The HRV parameters were obtained from the HRV logger application. Then, the participants were asked to randomly perform five patterns of BE, deep and slow breathing, and developed BE1-4, accompanied by a video guide. Then, posttest measurements were obtained. Between each breathing pattern, the participants were instructed to sit in a quiet room for 30 min as a withdrawal of intervention before starting the next BE (Figure 1). The overall program took approximately 4 hours to complete and was finished in a single day. The processes were as follows.
Interventions
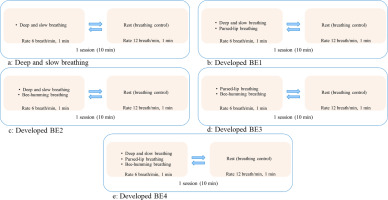
Deep and slow breathing: the participants inhaled deeply through both nostrils for 4 s, then exhaled slowly through both nostrils for 6 s (rate 6 breaths/min). After 1 min of deep and slow breathing, BC was performed at 12 breaths/min by breathing through both nostrils (inhale: exhale, 2:3) while placing the hand on the abdomen to feel the movement. This cycle was repeated for 10 min (Figure 2a).
The developed BE1 consists of deep and slow breathing and pursed-lip breathing. The participants inhaled deeply through both nostrils for 4 s, then exhaled slowly through both nostrils for 6 s. Then, deeply inhaled through both nostrils for 4 s and exhaled through the mouth while making an ‘O shape’ with the lips for 6 s. These were performed for 1 min, followed by a 1-min rest of BC. This cycle was repeated for 10 min (Figure 2b).
The developed BE2 consists of deep and slow breathing and bee-humming breathing. The participants inhaled deeply through both nostrils for 4 s, then exhaled slowly through both nostrils for 6 s. Then, deeply inhaled through both nostrils for 4 s, followed by a slow exhalation accompanied by a humming sound (‘MMMM’) for 6 s. These were performed for 1 min, followed by a 1-min rest of BC. This cycle was repeated for 10 min (Figure 2c).
The developed BE3 consists of pursed-lip breathing and bee-humming breathing. The participants repeatedly performed 1 set of pursed-lip breathing and 1 set of bee-humming breathing at a rate of 6 breaths/min for 1 min, followed by a 1-min rest of BC. This cycle was repeated for 10 min (Figure 2d).
The developed BE4 consists of deep and slow breathing, pursed-lip breathing, and bee-humming breathing. The participants repeatedly performed 1 set of deep and slow, 1 set of pursed-lip breathing, and 1 set of bee-humming breathing at a rate of 6 breaths/min for 1 min, followed by a 1-min rest of BC. This cycle was repeated for 10 min (Figure 2e).
The video guide provided a beep sound to control the breathing rate of the participants throughout the session.
Statistical analysis
Data analyses were conducted using the statistical software SPSS (version 29.0; SPSS Inc, Chicago, IL). Descriptive statistics were calculated to characterise the sample. The Shapiro–Wilk test was performed to assess the normality of the study variables’ distributions. A two-way analysis was used to determine whether the haemodynamics or HRV parameters were modulated after the BE session. The significant value was p < 0.05.
Results
Baseline characteristics
A total of 24 hypertensive patients were screened for this study, and 20 fulfilled the eligibility criteria. All participants completed the exercise sessions without dropping out. Table 1 shows the demographic characteristics, basic information about HT, and participant comorbidities.
Comparing the effect of breathing exercises on haemodynamics
The mean ± SEM values of haemodynamics are presented in Table 2. The analysis was performed to determined its effect on BP and HR. Two-way analysis revealed a significant effect of time on SBP (F(1,19) = 20.19, p < 0.05). SBP was significantly reduced throughout the 10-min session. The post hoc Bonferroni test indicated a significant reduction in SBP after the developed BE1, BE2, and BE3 were performed, at p < 0.05. However, there was no significant Intervention × time interaction effect or intervention effect that emerged for SBP. No significant intervention, time, and intervention × time effect emerged for DBP. In the analysis of HR, there was no significant difference between pre-test and post-test.
Table 1
Baseline characteristics
Comparing the effect of breathing exercises on HRV parameters
The normality distribution of the HRV parameters did not meet the assumption of normality, and a nonparametric test was conducted. A Friedman test was carried out to compare the effect of BE on the HRV parameters. There was a significant difference in the SDNN of the within-group comparison: χ2 (9) = 18.59, p < 0.05. Post hoc tests reported a significant difference between the pre-test and post-test of developed BEI, BE3, and BE4 at p < 0.05 as shown in Table 3. No between-groups comparison was performed.
Discussion
The main finding of this study is that the developed BE is more effective than the basic BE in modulating haemodynamics and HRV parameters. SBP was significantly reduced throughout the 10-min session by the effect of the time analysis of the developed BEI, BE2, and BE3, while the value of SDNN significantly increased immediately after performing the developed BE1, BE3, and BE4.
The significant effect of the time analysis revealed a shortterm effect on reducing the SBP of the developed BEI, BE2, and BE3, but it had no significant effect on the DBP or HR. The value of the mean difference of the SBP also supports these findings. There was a mean difference with a 95% CI of the SBP comparing post- to pre-intervention for developed BE1 [–5.5(–9.7, –1.2)], BE3 [–4.6(–7.1, –2.1)], BE2 [–3.6(–6.3, –0.8)], BE4 [–2.4(–5.3, 0.6)], and deep and slow [–1.3(–5.5, 3.0)]. All of them may contribute to a lower SBP. Even if the statistics analysis could not answer the research question of comparing the different effects of developed BE and basic BE, deep and slow breathing showed the smallest change in SBP compared to all the other groups. Regarding prior research, SBP was the most significant predictor of stroke morbidity risk in both middle-aged and older adults [13]. A 4-mmHg decrease in average SBP is estimated to reduce stroke mortality by 8.9% and 5.8%, respectively [13]. Therefore, the results summarised that the developed BE was more effective than the basic BE at modulating SBP. Moreover, the developed BE1 and three trends benefit hypertensive patients the most.
Regarding the HRV parameters, there was a significant difference between the pre-test and post-test of SDNN. Our study’s findings show the significant benefits of the developed BE1, BE3, and BE4 after 10 min of exercise sessions. At the same time, there was no significant difference between groups. The mean difference with a 95% CI of SDNN was revealed. There were developed BE1 [12.6(5.8, 19.5)], BE3 [7.3(2.2, 12.5)], BE4 [6.3(0.2, 12.3)], BE2 [5.1(–1.2, 11.4)], and deep and slow [–0.67(–9.5, 8.2)]. Deep and slow breathing demonstrated the smallest change in SDNN compared to all groups. Our results correspond with the previous study, which found that BE at a rate of 6 breaths/min had no consistent effect on the R-R interval while it is significantly increased in SDNN. They imply that this fluctuation has some effect on improving arterial baroreflex sensitivity [14]. Our results showed that the developed BE is more effective than the basic BE at increasing SDNN. Similar to SBP, the developed BE1 and three trends benefit hypertensive patients the most.
Table 2
Comparing effect of breathing exercise on haemodynamics
Table 3
Comparing effect of breathing exercise on HRV parameters
[i] SDNN – standard deviations of all the NN intervals, RMSSD – root mean square of successive differences between normal heartbeats, pNN50 – percentage of adjacent NN intervals that differ from each other by more than 50 ms, LF – low frequency, HF – high frequency, LF/HF ratio – low frequency per high frequency ratio
* p-value < 0.05 indicates significant as compared to baseline of each group
Following these results, developed BE seems better than deep and slow breathing at decreasing haemodynamics (SBP) and promoting the HRV parameter (SDNN). The best breathing pattern in our study for helping hypertensive patients control their clinical parameters are developed BE1 (deep and slow with pursed-lip) and BE3 (pursed-lip with bee-humming). It can therefore be assumed that a combination with pursed lips in the cycle appears more effective. These findings are related to previous investigations to our study. There were comparisons of deep and slow, pursed-lip and bee-humming breathing on haemodynamics. Pursed-lip revealed a significantly reduced SBP after 10 min of the exercise session (supplementary data).
According to a previous study, BE is associated with improved baroreflex sensitivity, which is potentially linked to a relative reduction in sympathetic activity or an increase in parasympathetic activity, contributing to a lower BP [15]. Alternatively, changes in chest expansion may increase the fluctuation in the R-R interval, which induces baroreflex to be more effective. On the other hand, an increase in tidal volume and activation of the Hering-Breuer reflex may reduce chemoreflex sensitivity and consequently highlight baroreflex efficacy, decreasing BP and sympathetic activity [16]. Fourthly, exhalation with an mouth open produces a small amount of positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP), supporting the patency of the airways in gas exchange and ventilation, leading to the modulation of chemoreceptors to stimulate baroreceptors and decreasing SBP [13]. Pursed-lip was linked to a combination of mechanisms, including increased parasympathetic tone due to deep, slow breathing, and reduced anxiety and stress as a result of mindfulness practices [8]. Lastly, the vibration of humming acts like an auditory stimulus that may stimulate the vagus nerve, thereby also contributing to parasympathetic tone [8, 9, 17, 18]. These mechanisms may simultaneously stimulate the baroreceptor, having the combined effect of haemodynamics and autonomic activity in developed BE groups. However, further study is needed to prove this effectiveness.
While other parameters were not changed, many factors might be responsible for these effects. Firstly, the participants were informed to consume everyday foods, and there was no record of food intake. The participants’ food may have contained a lot of salt, which can affect the BP [2]. Similar to the study by Zahroh and colleagues, there was no significant change in BP after 15 min of BE because over 80% of the respondents consumed salty foods [19]. Secondly, half of the participants in this study had a normal BP at baseline (Table 1). The participants were correctly taking antihypertensive drugs to control their BP. This is related to the research by Ghati et al. [9], who stated that taking adequate medicine may attenuate the influence of BE on BP [9]. Thirdly, the participants had time to practice the BE only before the experiment and had no previous training, which may have led to the lack of apparent modulation on all parameters. As mentioned by Ghati et al. [9], the participants who were not experienced with BE before the study may have had a high chance of underperforming during exercise sessions [9]. Our study’s participants also wore the spirometer’s mask during exercise sessions, which may have been uncomfortable. Nervousness and stress may alter the ANS, resulting in modulation of the HRV parameters [20]. Fourthly, after evaluating the power analysis, the small sample size impacted the results. Further study should involve a larger number of patients.
Conclusions
The developed BE is more effective than the basic BE (deep and slow) in lowering haemodynamics (SBP) and modulating HRV parameters (SDNN). A BE cycle combined with pursed-lip breathing (developed BE1 and BE3) effectively reduced the SBP and increased the SDNN throughout the 10-min session. These are complementary treatments for patients who have high blood pressure.