Introduction
Shoulder pain is a common reason for medical consultation, ranking third in musculoskeletal pain after back and knee pain [1]. The prevalence of shoulder pain is 1 to 4.8% in the general population, with around 50% experiencing persistent pain for over six months [1–3]
Subacromial impingement syndrome (SAiS) is the leading cause of shoulder pain, accounting for 44–65% of cases and primarily affecting women aged 45–64 [1, 4]. SAiS results in inflammation or rotator cuff tendon degeneration due to subacromial space conflicts (primary SAiS) or misalignment of the humeral head caused by muscle imbalances (secondary SAiS) [5]. Additionally, risk factors like smoking, sleep positions, repetitive shoulder activities, and acromion shape are important considerations [3]. SAiS has three clinical stages [6]: (1) oedema and inflammation with pain during and after movement; (2) fibrosis and tendinitis with inflammation, weakness, crepitus, limited range of motion (RoM), and arm-raising difficulty; and (3) osteophytes and subacromial tendon rupture. The first stage is more common in individuals under 25 years of age, while the latter two are more prevalent after 40 [1, 6].
SAiS treatment includes medications, injections, and surgery for severe cases, while conservative therapy emphasises physical therapy [7]. despite surgery rates, studies show no significant difference in pain and disability reduction compared to conservative management [1, 7]. different physical therapy modalities, such as shoulder girdle exercises, manual therapy, transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), and low-level laser therapy (LLLT), have proven to be effective in the treatment of SAiS [8–10].
LLLT effectively manages SAiS by reducing pain and enhancing RoM and functionality, especially when combined with exercises [10, 11]. LLLT is a safe, non-invasive photo-therapy using high-concentration red or infrared photons to modulate biological processes (photobiomodulation), with powers below 0.5 W that do not heat biological tissues [12, 13]. LLLT turns on enzymes in the respiratory chain (complex iV); increases ATP, dNA, and RNA synthesis; and increases metabolism. it also slows nerve conduction and releases -endorphins. it also reduces inflammatory mediators, promotes collagen production, and aids nerve regeneration [12–14].
In recent years, new treatment technologies involving high-power lasers (HiLT) have been developed for managing musculoskeletal pain [15, 16]. HiLT and LLLT share similar biophysical characteristics, differing only in their emission powers (HiLT being greater than 0.5 W). Higher power enables quicker energy delivery to tissues, resulting in varying degrees of heating and coverage of larger treatment areas [16].
Due to the growing interest in HiLT as a way to treat pain in the musculoskeletal system and the proven effectiveness of LLLT in SAiS, clinical trials (RCTs) have started to investigate the effects of HiLT in this condition [17–21]. However, given the novelty of this resource, there is uncertainty regarding the quantity, quality, and outcomes of these RCTs supporting HiLT for SAiS treatment. Consequently, the purpose of this systematic review (SR) is to assess the existing evidence regarding the effectiveness of HiLT as a therapy for SAiS.
Subjects and methods
Design
This SR followed PRiSMA guidelines and was registered in the National institute for Health Research’s international Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PRoSPERo) under id CRd42023387399 [22, 23].
The research question was structured using the PiCo approach (population, intervention, comparison, and outcome). The study focused on patients with SAiS who underwent HiLT, compared to those receiving other physical therapy interventions, with or without sham HiLT. The primary outcome assessed pain intensity changes using tools like the visual analogue scale (VAS), the numerical scale (NPRS), or other validated scales. Changes in RoM (measured by goniometry) and disability (measured with established questionnaires like the disability of Arm, Shoulder, and Hand Questionnaire, the Shoulder Pain and disability index [dASH], or the Constant-Murley Shoulder outcome Score, [CMS]) were considered secondary outcomes.
Search strategy
Medline (via PubMed), Web of Science, Scopus, CiNAHL, Science direct, Cochrane Library, the Evidence-Based Physiotherapy database (PEdro), and Google Scholar databases were searched for HiLT in SAiS RCTs (updated to January 8, 2025). The search was conducted employing a curated set of keywords extracted from the MeSH (Medical Subject Headings) dictionary. These keywords encompassed “Lasers”, “Laser Therapy”, “Phototherapy”, “High-intensity Laser Therapy”, “Class iV laser”,“Musculoskeletal Pai”, “Shoulder Pain”, “Shoulder impingement Syndrome”, “Joint diseases”, and “Rotator Cuff Tear Arthropathy”. These terms were combined using boolean connectors “oR” and “ANd” to create the search algorithm: (((((“Lasers”) OR (“Laser Therapy”)) OR (“Phototherapy”)) OR (“High-Intensity Laser Therapy”)) OR (“Class IV laser”)) AND (((((“Musculoskeletal Pain”) OR (“Shoulder Pain”)) OR (“Shoulder Impingement Syndrome”)) OR (“Joint Diseases”)) OR (“Rotator Cuff Tear Arthropathy”)). Furthermore, filters for “Clinical Trial” and “Randomised Controlled Trial” were used to ensure the identification of clinical trials in the search results.
Selection criteria
Three independent researchers (AC-B, FP-A, and ES-o) collectively assessed article titles and abstracts from the databases using the Rayyan web tool (https://www.rayyan.ai/), making inclusion or exclusion decisions based on predefined criteria. The review used the following inclusion criteria: (A) human clinical trials with a SAiS diagnosis, (B) studies in English, Portuguese or Spanish, (C) HiLT alone or in combination with other physical therapy modalities, (d) comparisons with other physical therapy treatments with or without placebo, and (E) changes in pain intensity measured by different scales or instruments as the main outcome. Exclusions comprised literature reviews, systemic reviews of HiLT and SAiS linked to other musculoskeletal or neurological disorders, and studies with incomplete or inaccessible texts. No time limitation has been set for the search, considering the recent emergence of HiLT and the potential limitation in the quantity of available studies.
Risk of bias (RoB)
The RCTs’ methodological quality was initially assessed using the PEdro scale (iCC 0.53–0.91) for an initial overview [24]. Additionally, researchers used the Cochrane Collaboration risk of bias 2 tool (RoB 2.0) to evaluate bias based on investigator judgment [25]. Studies with PEdro scores above five were categorised as having good (6–8 points) or excellent methodological quality (9–10 points). Using the RoB tool, studies with two or more high RoBs were deemed low quality [25]. Concordance in RoB evaluation among researchers was assessed using the kappa statistic [26].
Statistical analysis
For statistical analysis, the Review Manager Software (RevMan 5.4) from the Cochrane Collaboration was utilised [27]. Heterogeneity across studies was evaluated using the chi-square ( 2) test and the I2 statistic, categorised as follows: unimportant (0–40%), moderate (30–60%), substantial (50–90%), or considerable (75–100%). depending on the degree of heterogeneity observed, the researchers employed either the Mantel-Haenszel fixed-effects method or the derSimonian and Laird random-effects method to calculate the pooled effect using mean differences (Mds) for the outcomes of interest, along with their corresponding 95% confidence intervals (Ci) [28].
Evidence recommendation
The evaluation of the quality of evidence employed the GRAdE approach (Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, development, and Evaluation), considering criteria such as RoB, inconsistency, indirectness of evidence, imprecision, and publication bias [29]:
RoB. Highs are present if there are deficiencies in blinding or hidden allocation criteria, potentially leading to an overestimation of treatment effects.
Inconsistency. depends on heterogeneity equal to or exceeding 50% for an interesting outcome.
Indirect evidence. identified when the characteristics of treated individuals deviated from those of the broader population with the health condition or when comparing HiLT treatment to less common interventions in the available evidence or clinical practice.
Imprecision. depends on whether the Cis for the pooled effect in meta-analyses intersect the line of no effect, which suggests a lack of clarity in favouring one of the two treatment groups. Furthermore, the optimal sample size will be evaluated, requiring a representative participant number exceeding 200 to consider the effect as clinically relevant.
Publication bias. depends on the number of studies related to the relevant outcome, with a cutoff of at least three studies to mitigate bias effectively.
Evidence levels, ranging from high to very low, were assigned, with an initial high-quality rating for each level due to the exclusive inclusion of RCTs in this review [29]. Factors affecting one or two GRAdE domains may potentially lead to a downgrade of the evidence quality by one or two levels. The assessment of evidence importance will involve a comparison to ascertain whether statistically significant weighted Mds align with the literature’s definition of minimal clinically important differences (MCid).
To ensure a comprehensive synthesis of evidence regarding HiLT and its effects in SAiS, researchers used the GRAdEpro GdT tool for guideline development to facilitate a summary table of evidence for outcomes that demonstrated statistical significance in the meta-analysis (https://www.gradepro.org).
Results
Search results
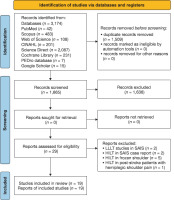
The initial database search generated a preliminary 3,174 articles (PubMed = 42; Scopus = 483; Web of Science = 108; CiNAHL = 201; Science direct = 2,087; Cochrane Central = 201; the PEdro database = 7; and Google Scholar = 15). Following the removal of duplicate articles, 29 documents remained for further analysis. However, ten articles were excluded as they pertained to studies on HiLT for frozen shoulder (n = 5), LLLT in SAiS (n = 2), two case reports (n = 2), and HiLT in post-stroke patients with hemiplegic shoulder pain (n = 1). This led to a final selection of 19 articles for analysis [17–21, 30–43]. Figure 1 illustrates the PRiSMA flowchart outlining the article search and selection process.
Appendix 1 provides a summary of the search strategy and results for each database.
Methodological quality and risk of bias
Methodological quality assessed by the PEdro scale indicated an overall good-to-excellent quality, averaging 7 points (Table 1) [24]. Major methodological gaps were noted in the concealment allocation and blinding of participants and assessors. However, criteria such as random participant assignment, pre-treatment group comparisons, participant follow-up, and intergroup treatment comparisons were generally fulfilled.
Table 1
Characteristics of studies comparing H i LT for shoulder impingement syndrome
| No. | Author (year) country | Study | PEdro score | Total (n) group composition (n) Mean age (mean ± SD) | inclusion criteria | Exclusion criteria | intervention | HiLT dose | Sessions | outcomes | Evaluations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Santamato et al.(2009) [17]italy | Short-term effects of high-intensity laser therapy versus ultrasound therapy in the treatment of people with subacromial impingement syndrome: a randomized clinical trial | 8/10 | n = 70 EG = 35 (15, 20) CG = 35 (13, 22) 54.1 ± 9.0 | EG: HiLT CG: US | 10 s (2 weeks) | T0: baseline T1: post-treat-ment (2 weeks) | ||||
| 2 | Ghomi et al.(2014) [18]iran | The comparison of high-power laser and routine physiotherapy in the treat-ment of supraspinatus tendinitis | 8/10 | n = 40 EG = 20 (8, 12) CG = 20 (9, 11) 38.3 ± 9.0 | EG: HiLT + US + TENS + TE CG: US + TENS + TE | 6 s (2 weeks) | T0: baseline T1: post-treat-ment (2 weeks) | ||||
| 3 | Karaca(2016) [19]Turkey | Effectiveness of high-intensity laser therapy in subacromial impingement syndrome | / | n = 42 EG = 42 (17 , 25 ) 56.6 ± 11.2 | EG: HiLT | 9 s (3 weeks) | T0: baseline T1: post-treat-ment (3 weeks) | ||||
| 4 | Pekyavas and Baltaci(2016) [20]Turkey | Short-term effects of high-intensity laser therapy, manual therapy, and Kinesio taping in patients with subacromial impingement syndrome | 6/10 | n = 70 EG = 19 (NS) CG1 = 15 (NS) CG2 = 20 (NS) CG3 = 16 (NS) age NS | EG: HiLT + manual therapy + KT + TE CG1: TE CG2: KT + TE CG3: manual therapy + KT + TE | 15 s (3 weeks) | T0: baseline T1: post-treat-ment (3 weeks) | ||||
| 5 | Ökmen et al.(2017) [21]Turkey | Comparison of the efficacy of high intensity laser and ultrasound therapies in chronic shoulder pain; randomized controlled single blind study | 6/10 | n = 141 EG = 71 (22, 49) CG = 70 (23, 7) 58.5 ± 9.6 | EG: HiLT + HP + TENS+balneao-therapy + TE CG: US + HP + TENS+balneao-therapy + TE | 14 s (2 weeks) | T0: baseline T1: post-treat-ment (3 weeks) T2: follow-up (1 month) | ||||
| 6 | Zafar and Kumar(2017) [30]india | Comparison of laser and ultrasound therapy for the management of shoulder rotator cuff muscles injury | 7/10 | n = 20 EG = 10 (10, 0) CG = 10 (10, 0) 33.6 ± 4.2 | EG: HiLT + TE CG: US + TE | 20 s (4 weeks) | T0: baseline T1: during treatment (3 weeks) T2: post-treat-ment (4 weeks) | ||||
| 7 | Zafar and Kumar(2017) [31]india | Role of ultrasound with laser to improve function in rotator cuff injury for age group 40–55 years | 7/10 | n = 20 EG = 10 (10, 0) CG = 10 (10, 0) 46.2 ± 8.1 | EG: HiLT + TE CG: US + TE | 20 s (4 weeks) | T0: baseline T1: post-treat-ment (4 weeks) T2: post-treat-ment (12 weeks) | ||||
| 8 | Ökmen and Ökmen(2017) [32]Turkey | Comparison of photobio-modulation therapy and suprascapular nerve-pulsed radiofrequency in chronic shoulder pain: a randomized controlled, single-blind, clinical trial | 5/10 | n = 59 EG = 29 (12, 17) CG = 30 (13, 17) 52.4 ± 8.7 | EG: HiLT CG: radiofre-cuency | 12 s (4 weeks) | T0: baseline T1: post-treat-ment (2 weeks) T2: follow-up (1 month) T3: follow-up (3 months) T4: follow-up (12 months) | ||||
| 9 | Elsodany et al.(2018) [33]Egypt | Long-term effect of pulsed Nd:YAG laser in the treatment of patients with rotator cuff tendinopathy: a randomized controlled trial | 5/10 | n = 60 EG = 30 (NS) CG = 30 (NS) 50.2 ± 3.6 | EG: HiLT + TE CG: TE | 14 s (2 weeks) | T0: baseline T1: post-treat-ment (4 weeks) T2: follow-up (3 months) T3: follow-up (6 months) | ||||
| 10 | Aceituno-Gómezet al. (2019) [34]Spain | Efficacy of high-intensity laser therapy in subacromial impingement syndrome: a three-month follow-up controlled clinical trial | 6/10 | n = 43 EG = 21 (7, 16) CG = 22 (11, 12) 59.0 ± 8.9 | EG: HiLT + TE CG: Sham HiLT + TE | 15 s (3 weeks) | T0: baseline T1: post-treat-ment (2 weeks) T2: follow-up (1 month) T3: follow-up (3 months) | ||||
| 11 | Cheng et al.(2020) [35]Taiwan | The immediate effect of high-intensity laser therapy on pain relief and shoulder function in patients with subacromial impingement syndrome | / | n = 20 EG = 20 (8, 12) 50.5 ±6.6 |
| EG: HiLT | 15 s (3 weeks) | T0: baseline T1: post-treat-ment (1 day) | |||
| 12 | Kamal et al.(2020) [36]Egypt | Effect of high-power laser on shoulder mobility in sub acromial impingement syndrome: randomized controlled trial | 7/10 | n = 40 EG = 20 (10, 10) CG = 20 (10, 10) 37.1 ± 11.3 | EG: HiLT + TE CG: TE | 12 s (6 weeks) | T0: baseline T1: post-treat-ment (6 weeks) | ||||
| 13 | Kamal et al.(2021) [37]Egypt | High-power laser versus phonophoresis in subacro-mial impingement syndrome: randomized controlled trial | 7/10 | n = 40 EG = 20 (10, 10) CG = 20 (10, 10) 37.1 ± 11.4 | EG: HiLT + TE CG: phono-foresis + TE | 12 s (6 weeks) | T0: baseline T1: post-treat-ment (6 weeks) | ||||
| 14 | Sirbu et al.(2021) [38]Romania | The short-term outcomes of Multiwave Locked System (MLS) laser therapy versus a combination of transcuta-neous nerve stimulation and ultrasound treatment for subacromial pain syndrome | 5/10 | n = 47 EG = 22 (9, 13) CG = 25 (13, 12) 58.6 ± 10.2 | EG: HiLT + TE CG: US + TENS + TE | 10 s (3 weeks) | T0: baseline T1: post-treat-ment (3 weeks) | ||||
| 15 | Aydin et al.(2021) [39]Turkey | The effect of high-intensity laser therapy on pain and functionality in patients with chronic shoulder pain | 6/10 | n = 56 EG = 28 (13, 15) CG = 28 (17, 8) 64.3 ±7.25 | EG: HiLT + US + TENS + iTFC + HP + TE CG: US + TENS + iTFC + HP + TE | 15 s (3 weeks) | T0: baseline T1: post-treat-ment (3 weeks) | ||||
| 16 | dost and Eken (2021) [40]Turkey | Comparison of the efficacy of high intensity laser and ultrasound therapies in shoulder impingement syndrome: a randomized clinical trial | n = 70 EG = 35 (14, 21) CG = 35 (12, 23) 47.1 ± 8.7 | EG: HiLT CG: US | 10 s (2 weeks) | T0: baseline T1: post-treat-ment (2 weeks) T2: follow-up (4 weeks) | |||||
| 17 | Zaki et al.(2022) [41]iran | Comparison of low level and high power laser combined with kinesiology taping on shoulder function and musculoskeletal sonography parameters in subacromial impingement syndrome: a randomized placebo-controlled trial | 8/10 | n = 30 EG = 10 (5, 5) CG1 = 10 (4, 6) CG2 = 10 (4, 6) 48.6 ± 12.8 | EG: HiLT + KT CG1: LLLT + KT CG2: sham HiLT + KT | 7 s (2 weeks) | T0: baseline T1: post-treat-ment (2 weeks) | ||||
| 18 | Yilmaz et al, (2022) [42] Turkey | The effectiveness of high- intensity laser therapy on pain, range of motion, functional capacity, quality of life, and muscle strength in subacromial impingement syndrome: a 3-month followup, double-blinded, randomized, placebo-controlled trial | 8/10 | n = 63 EG = 32 (11, 21) CG = 31 (10, 21) 50.7 ± 7.6 | EG: HILT + TE CG: sham HILT + TE |
| 15 s (3 weeks) | TO: baseline T1: post-treatment (3 weeks) T2: follow-up (12 weeks) | |||
| 19 | Yeşilyaprak et al, (2023) [43] Turkey | The addition of exercise to high-intensity laser therapy improves treatment effectiveness on pain and muscle strength in patients with subacromial pain syndrome: a randomized trial | 8/10 | n = 30 EG1 = 15(11, 4) EG2 = 15(7, 8) 49.6 ± 9.6 | EG1: HILT EG2: HILT + TE | 10 s (3 weeks) | TO: baseline T1: post-treatment (3 weeks) |
[i] ABD – abduction, ALG – algometry, BMI – body mass index, CG – control group, CMS – Constant-Murley Scale, DASH – disabilities of the arm, shoulder and hand, DNM – dynamometry, EG – experimental group, ER – external rotation, FLEX – flexion, GNM – goniometry, HILT – high-intensity laser therapy, HP – hydrocollator pack, IR – internal rotation, ISK – isokinetic strength evaluation, ITFC – interferential currents, KT – kinesiotape, LLLT – low-level laser therapy, MRI – magnetic resonance imaging, MSKUS – musculoskeletal ultrasound, Nd:YAG – neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet, NHP – Nottingham Health Profile, NS – not specifics, PI – pain intensity, PT – physical therapy, PPT – pain pressure threshold, Q-DASH – quick disabilities of the arm, shoulder and hand, QoL – quality of life, ROM – range of motion, SAIS – subacromial impingement syndrome, SF-36 – short-form 36 health survey, SPADI – shoulder pain and disability index, SST – Simple Shoulder Test, TE – therapeutic exercise, TENS – transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation, UCLA – University of California Los Angeles Questionnaire, US – therapeutic ultrasound, USG – ultrasonography, VAS – visual analogue scale
Figure 2 shows the RoB 2.0 assessment conducted by three investigators (HdB, ACB, and NSV) on the included studies. The RoB assessments resulted in a consensus among evaluators, with a kappa coefficient of 0.90. The primary high RoB was linked to measurements in the outcome data (57.7%) and bias due to deviations from the intended intervention (26.0%). Conversely, bias in the measure of outcome data (0%), bias in missing outcome data (89.4%), and bias in the randomisation process (15.7%) were deemed to have a low RoB. Considering the presence of these results, they yielded an overall risk of (31.6%).
Characteristics of the RCTs
Table 1 provides a concise overview of essential details from the RCTs, encompassing study groups, selection criteria, interventions, assessments, and relevant outcomes. These trials were conducted across various countries, including italy [17], iran [18, 41], Turkey [19–21, 32, 39, 40, 43], india [30, 31], Egypt [33, 36, 37], Taiwan [35], Spain [34], and Romania [38], spanning from 2009 to 2023.
A total of 871 participants diagnosed with SAiS were included, with an average age of 46.9 years (Sd ± 8.8), comprised of 379 women and 322 men, and two studies lacked gender information. Among these, 449 received HiLT, while 422 controls underwent conventional physical therapy. in the experimental group (EG), 141 patients exclusively received HiLT [17, 19, 32, 35, 40], and 308 participants received HiLT alongside US [18, 39], therapeutic exercises [18, 20, 21, 30, 31, 33, 34, 36–38, 43], TENS [18, 20, 21, 39], thermotherapy [21, 39], Kinesio Tape [20,42], and interferential current [39]. Controls (GCs) were treated with US [17, 18, 30, 31, 38–41], therapeutic exercises [18, 20, 21, 30, 31, 33, 34, 36–38, 43], interferential current [39], radiofrequency [32], thermotherapy [21, 41], Kinesio Tape [20, 41], and LLLT [41]. Furthermore, two studies employed placebo HiLT [34, 41, 42].
HiLT treatments primarily targeted the deltoid, with the scanning technique being the predominant approach in most studies [17–21, 30–32, 34, 35, 38, 39]. Six studies utilised a combination of scanning and spot techniques [33, 36, 37, 41–43], while the spot technique alone was used in one RCT [40]. in 12 studies, 1064 nm Nd:YAG lasers were used [17, 19–21, 32–34, 36, 37, 39, 42, 43], while dual-wavelength devices (808–930 nm) were employed in 3 studies [35, 38, 41], and four studies used three different wavelengths within the infrared spectrum [18, 30, 31, 40]. The maximum power output ranged from 1.5 to 3000 W, with 8 and 12 W being the most common. The average energy delivered typically fell within the range of 2500–3000 J. The number of treatment sessions varied, ranging from 10 to 15 sessions over a span of 3 to 4 weeks. Additional HiLT parameters, such as pulse rate, phase duration, energy density, and treatment duration, are summarised in Table 1.
Outcomes
In these studies, pain intensity was assessed via VAS [17–21, 30–35, 37, 37–43], while the SPAdi was employed to evaluate shoulder pain [20, 21, 30, 32, 40, 41] and disability. Shoulder RoM was quantified using goniometry [20, 31, 33, 35–37, 39, 42, 43]. Also, pain pressure threshold [39,40], functional assessment with CMS [17, 34, 35, 38, 42, 43], quality of life with SF-36 [42] and NHP [32], tendon thickness with ultrasonography [36, 37], and muscle strength with dynamometry [39] or isokinetic assessment [42] were important outcomes.
Table 2 shows the results and comparisons between the studies and control groups. Both groups experienced a significant reduction in pain (p < 0.05) during the evaluation sessions [17–21, 30–43]. However, HiLT demonstrates a more pronounced and lasting pain reduction after treatment and during follow-up sessions. For RoM and disability, both groups exhibit statistically significant differences before and after treatment (p < 0.05). HiLT notably enhances RoM, but findings regarding disability are mixed, with conflicting results in certain studies [20, 21, 39].
Table 2
Outcomes and statistical comparisons for H i LT groups in the included studies
| Study | Outcome | HILT | CG | p-value intergroup posttreatment | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TO: baseline | T1: posttreatment | T2: follow-up | T3: follow-up | p-value intragroup T0-T1 | p-value intragroup T0-T2 | p-value intragroup T0-T3 | TO: baseline | T1: posttreatment | T2: follow-up | T3: follow-up | p-value intragroup T0-T1 | p-value intragroup T0-T2 | p-value intragroup T0-T3 | |||||||||||
| Santamato et al. (2009) [17] | PI (VAS, cm) mean ± SD | 6.3 ± 1.8 | 2.4 ± 1.4 (2 weeks) | / | <0.01* | / | 6.6 ± 1.5 | 4.4 ± 1.4 (2 weeks) | / | <0.01* | / | <0.01* | ||||||||||||
| Function (CMS, score) mean ± SD | 63.2 ± 8.7 | 75.9 ±7.0 (2 weeks) | 63.1 ± 7.1 | 72.1 ±7.0 (2 weeks) | 0.03* | 0.03* | ||||||||||||||||||
| Function (SST, score) mean ± SD | 7.2 ± 2.3 | 9.7 ±2.0 (2 weeks) | 6.9 ± 2.2 | 8.7 ± 2.0 (2 weeks) | 0.06 | 0.06 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Ghomi et al. (2014) [18] | PI (VAS, cm) mean ± SD | 7.6 ± 0.8 | 3.5 ± 1.5 (2 weeks) | / | <0.05* | / | 7.2 ± 1.3 | 5.03 ± 1.5 (2 weeks) | / | < 0.05* | / | < 0.05* | ||||||||||||
| Disability (DASH,%) mean ± SD | 58.8 ± 12.5 | 33.6 ±6.8 (2 weeks) | 51.8 ± 11.9 | 45.7 ± 1.0 (2 weeks) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Karaca (2016) [19] | PI (SPADI,%) median(IQR) | 31(17-50) | 10(0-46) (3 weeks) | / | <0.01* | / | without CG | N/A | ||||||||||||||||
| Disability (SPADI,%) median(IQR) | 42(12-80) | 20(0-56) (3 weeks) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function (UCLA, score) median(IQR) | 20(11-26) | 29(16-35) (3 weeks) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pekyavas and Baltaci (2016) [20] | PI (VAS, cm) | NS | / | NS | / | NS | / | NS | / | NS | ||||||||||||||
| PI (SPADI,%) mean ± SD | 76.4 ±4.9 | 4.2 ±5.1 (3 weeks) | 0.000* | 65.8 ± 12.6 | 13.1 ± 13.2 (3 weeks) | < 0.05* | 0.967 | |||||||||||||||||
| Shoulder0ER (GNM,grades) mean ± SD | 49.7 ± 23.0 | 78.6 ± 11.8 (3 weeks) | 72.0 ± 19.9 | 82.8 ±8.8 (3 weeks) | 0.073 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Shoulder ABD (GNM, grades) mean ± SD | 130.3 ± 31.1 | 167.8 ±9.2 (3 weeks) | 157.2 ± 28.0 | 173.7 ±2.7 (3 weeks) | 0.031* | |||||||||||||||||||
| Shoulder FLEX (GNM, grades) mean ± SD | 140.0 ± 29.4 | 172.4 ±7.4 (3 weeks) | 160.9 ± 23.5 | 176.5 ±2.7 (3 weeks) | 0.265 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Disability (SPADI, %) mean ± SD | 80.2 ± 13.1 | 7.4 ±4.5 (3 weeks) | 58.6± 21.9 | 14.6 ± 12.3 (3 weeks) | 0.906 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Ökmen et al. (2017) [21] | PI (VAS, cm) mean ± SD | 6.6 ± 1.6 | 4.6. ± 1.7 (2 weeks) | 2.67 ± 1.3 (4 weeks) | / | <0.01* | / | 6.9 ± 1.9 | 5.5 ± 1.7 (2 weeks) | 4.2 ± 1.4 (4 weeks) | / | <0.001* | / | 0.003* | ||||||||||
| PI (SPADI,%) mean ± SD | 24.4 ± 10.2 | 25.2 ±8.8 (2 weeks) | 15.5 ± 7.2 (4 weeks) | 36.1 ± 9.4 | 28.4 ± 9.0 (2 weeks) | 23.4 ± 8.0 (4 weeks) | 0.034* | |||||||||||||||||
| Disability (SPADI, %) mean ± SD | 45.1 ± 17.9 | 33.2 ± 14.5 (2 weeks) | 21.1 ± 11.5 (4 weeks) | 49.2 ± 16.5 | 39.3 ± 14.8 (2 weeks) | 32.5 ± 13.0 (4 weeks) | 0.015* | |||||||||||||||||
| Zafar and Kumar (2017) [30] | PI (VAS,cm) mean ± SD | 7.5 ± 0.5 | 5.2 ±0.6 (3 weeks) | 3.2 ± 0.6 (4 weeks) | / | <0.001* | / | 7.6 ± 0.8 | 6.9 ± 0.5 (3 weeks) | 6.1 ± 1.0 (4 weeks) | / | <0.01* | / | <0.001* | ||||||||||
| PI (SPADI,%) mean ± SD | 33.1 ± 3.7 | 30.1 ±4.8 (3 weeks) | 22.6 ± 7.0 (4 weeks) | 36.8 ± 2.0 | 33.2 ±4.7 (3 weeks) | 22.9 ±4.5 (4 weeks) | 0.431 | |||||||||||||||||
| Shoulder FLEX (GNM, grades) mean ± SD | 51.3 ± 6.6 | 69.4 ±5.9 (3 weeks) | 90.4 ± 5.9 (4 weeks) | 53.6 ± 8.5 | 60.7 ± 5.8 (3 weeks) | 66.9 ± 5.7 (4 weeks) | <0.001* | |||||||||||||||||
| Shoulder ABD (GNM, grades) mean ± SD | 53.5 ± 6.3 | 70.2 ±4.6 (3 weeks) | 93.8 ± 3.7 (4 weeks) | 54.1 ± 7.0 | 57.4 ±4.5 (3 weeks) | 61.5 ±4.9 (4 weeks) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Disability (SPADI,score) mean ± SD | 52.0 ± 5.7 | 36.1 ±3.2 (3 weeks) | 20.5 ± 2.9 (4 weeks) | 56.7 ± 3.4 | 49.9 ±5.8 (3 weeks) | 46.8 ± 9.9 (4 weeks) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Zafar and Kumar (2017) [31] | Shoulder FLEX (GNM, grades) mean ± SD | 47.0 ± 3.9 | 96.8 ±4.0 (4 weeks) | 133.1 ± 2.3 (12 weeks) | / | <0.001* | / | 45.8 ± 6.5 | 82.3 ±4.4 (4 weeks) | 122.9 ± 3.8 (12 weeks) | / | <0.001* | / | <0.001* | ||||||||||
| Shoulder ABD (GNM, grades) mean ± SD | 46.8 ± 3.6 | 98.2 ±3.5 (4 weeks) | 133.6 ± 1.2 (12 weeks) | 44.2 ± 5.1 | 81.0 ± 2.5 (4 weeks) | 120.4 ± 2.6 (12 weeks) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Shoulder ER (GNM, grades) mean ± SD | 29.9 ± 2.2 | 60.7 ±3.0 (4 weeks) | 71.2 ± 2.5 (12 weeks) | 28.6 ± 1.4 | 55.3 ± 2.0 (4 weeks) | 63.4 ± 1.3 (12 weeks) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Shoulder IR (GNM, grades) mean ± SD | 33.8 ± 3.6 | 53.5 ± 2.5 (4 weeks) | 63.9 ± 1.6 (12 weeks) | 29.3 ± 2.6 | 49.6 ± 2.6 (4 weeks) | 59.9 ± 1.3 (12 weeks) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Ökmen and Ökmen (2017) [32] | PI(VAS,cm) median(IQR) | 6.3(19-85) | 2.0(8-40) (2 weeks) | 1.3(0-6.1) (4 weeks) | 2.0(0.8-4.0) (12 weeks) | <0.001* | 6.4(1.9-8.5) | 2.0(0.8-4.0) (2 weeks) | 1.6(0-6.1) (4 weeks) | 2.2(0.8-4.0) (12 weeks) | <0.01* | 0.952 | ||||||||||||
| PI (SPADI,%) median(IQR) | 39(19-48) | 11 (0-39) (2 weeks) | 8(0-41) (4 weeks) | 12(0-39) (12 weeks) | 37.5(19-48) | 11.5(0-39) (2 weeks) | 10(0-41) (4 weeks) | 13.5(2-39) (12 weeks) | 0.715 | |||||||||||||||
| Disability (SPADI,%) median(IQR) | 47(26-73) | 12(1-47) (2 weeks) | 7(0-53) (4 weeks) | 13(2-47) (12 weeks) | 45.5(26-73) | 11(1-47) (2 weeks) | 11 (0-53) (4 weeks) | 14(2-47) (12 weeks) | 0.988 | |||||||||||||||
| QoL (NH,score) median(IQR) | 308.9 (97-502.3) | 202.8 (10-502.3) (2 weeks) | 79.3 (0-391.9) (4 weeks) | 75.4 (0-330.4) (12 weeks) | 289.3 (41.4-502.3) | 147.6 (0-468.2) (2 weeks) | 78.4(0-468.2) (4 weeks) | 76.5(0-254.2) (12 weeks) | 0.103 | |||||||||||||||
| Elsodany et al, (2018) [33] | PI (VAS,cm) mean ± SD | 7.9 ± 0.6 | 1.8 ±0.6 (4 weeks) | 1.9 ± 0.6 (12 weeks) | 1.8 ±0.6 (24 weeks) | <0.001* | 7.7 ± 1.0 | 4.3 ± 0.7 (4 weeks) | 4.7 ± 0.5 (12 weeks) | 4.9 ± 0.7 (24 weeks) | <0.001* | <0.001* | ||||||||||||
| Active shoulder ABD (GNM,grades) mean ± SD | 92.9 ± 10.8 | 132.3 ±9.8 (4 weeks) | 132.2 ± 9.8 (12 weeks) | 132.1 ±9.9 (24 weeks) | 91.9± 10.2 | 112.5±9.8 (4 weeks) | 110.8 ± 9.6 (12 weeks) | 110.1 ± 9.6 (24 weeks) | ||||||||||||||||
| Passive shoulder ABD (GNM,grades) mean ± SD | 137.8 ± 6.8 | 168.5 ±6.2 (4 weeks) | 168.3 ± 6.2 (12 weeks) | 168.1 ±6.5 (24 weeks) | 136.3 ± 5.6 | 158.7 ± 5.9 (4 weeks) | 157.2 ± 6.2 (12 weeks) | 155.8 ± 6.1 (24 weeks) | ||||||||||||||||
| Active shoulder ER (GNM,grades) mean ± SD | 39.9 ± 3.3 | 75.3 ± 3.3 (4 weeks) | 75.1 ± 3.4 (12 weeks) | 75.0 ±3.5 (24 weeks) | 39.5 ± 2.7 | 56.9 ± 3.6 (4 weeks) | 56.8 ± 3.9 (12 weeks) | 55.3 ± 3.8 (24 weeks) | ||||||||||||||||
| Passive shoulder ER (GNM, grades) mean ± SD | 53.9 ± 3.5 | 80.1 ± 3.3 (4 weeks) | 97.9 ± 3.3 (12 weeks) | 97.8 ± 3.4 (24 weeks) | 55.1 ±3.1 | 65.5 ± 3.6 (4 weeks) | 64.9 ± 3.6 (12 weeks) | 64.3 ± 3.7 (24 weeks) | ||||||||||||||||
| Active shoulder IR (GNM, grades) mean ± SD | 29.5 ±2.9 | 53.3 ± 2.5 (4 weeks) | 53.1 ± 2.5 (12 weeks) | 52.9 ± 2.4 (24 weeks) | 28.6 ±2.6 | 44.0 ± 2.3 (4 weeks) | 39.7 ±2.5 (12 weeks) | 39.3 ± 2.5 (24 weeks) | ||||||||||||||||
| Passive shoulder IR (GNM, grades) mean ± SD | 53.6 ±3.6 | 80.1 ± 3.3 (4 weeks) | 79.9 ± 3.3 (12 weeks) | 79.9 ± 3.3 (24 weeks) | 55.1 ±3.1 | 65.5 ± 3.6 (4 weeks) | 63.9 ±3.5 (12 weeks) | 63.5 ±3.5 (24 weeks) | ||||||||||||||||
| Disability (SPADI,%) mean ± SD | 75.1 ±2.9 | 21.9± 1.3 (4 weeks) | 22.0 ± 1.3 (12 weeks) | 22.0 ± 1.2 (24 weeks) | 75.9 ±2.6 | 35.8 ± 1.9 (4 weeks) | 41.1 ±2.8 (12 weeks) | 41.4 ±2.6 (24 weeks) | ||||||||||||||||
| Aceituno-Gómez et al. (2019) [34] | PI (VAS, cm) mean ± SD | 5.4 ± 1.5 | 3.6 ± 1.9 (2 weeks) | 3.6 ± 2.4 (4 weeks) | 1.8 ± 1.8 (12 weeks) | <0.001* | 6.2 ± 1.0 | 4.1 ± 1.8 (2 weeks) | 3.0 ± 2.6 (4 weeks) | 2.6 ± 2.4 (12 weeks) | <0.001* | NS | ||||||||||||
| PPT (ALG, kg/cm2) mean ± SD | 2.5 ± 0.9 | 3.4 ± 1.0 (2 weeks) | 3.6 ± 1.1 (4 weeks) | 4.4 ± 1.2 (12 weeks) | 2.9 ± 0.6 | 3.5 ± 0.9 (2 weeks) | 4.0 ± 1.0 (4 weeks) | 4.4 ± 1.5 (12 weeks) | > 0.05 | < 0.05* | ||||||||||||||
| Disability (SPADI,%) mean ± SD | 41.8 ± 20.6 | 20.2 ± 16.1 (2 weeks) | 20.5 ± 19.8 (4 weeks) | 11.0 ± 14.5 (12 weeks) | 51.8 ± 16.1 | 23.0 ± 17.2 (2 weeks) | 16.3 ± 16.1 (4 weeks) | 13.6 ± 17.1 (12 weeks) | <0.001* | |||||||||||||||
| Function (CMS, score) mean ± SD | 49.9 ± 10.4 | 61.6 ±9.6 (2 weeks) | 65.2 ± 8.0 (4 weeks) | 68.5 ±7.4 (12 weeks) | 41.7 ± 9.8 | 57.5 ± 9.0 (2 weeks) | 62.9 ± 9.9 (4 weeks) | 66.3 ± 8.9 (12 weeks) | ||||||||||||||||
| Disability (Q-DASH, %) mean ± SD | 39.2 ± 16.0 | 19.5 ± 13.2 (2 weeks) | 17.7 ± 18.5 (4 weeks) | 9.9 ± 10.7 (12 weeks) | 46.2 ± 16.1 | 23.1 ± 16.6 (2 weeks) | 17.5 ± 17.0 (4 weeks) | 14.8 ± 17.1 (12 weeks) | ||||||||||||||||
| Cheng et al. (2020) [35] | PI (VAS, cm) mean ± SD | 6.6 ± 0.9 | 3.1 ± 0.6 (1 day) | / | < 0.05* | / | without CG | N/A | ||||||||||||||||
| Shoulder FLEX (GNM, grades) mean ± SD | 126 ± 15 | 138± 17 (1 day) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function (CMS, score) mean ± SD | 38 ±4 | 59 ± 7 (1 day) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kamal et al. (2020) [36] | PI (VAS, cm) mean ± SD | 6.7 ± 0.6 | 1.5± 0.4 (6 weeks) | / | <0.01* | / | 6.5 ± 0.6 | 3.7 ± 0.7 (6 weeks) | / | <0.01* | / | <0.01* | ||||||||||||
| Shoulder ABD (GNM, grades) mean ± SD | 105.1 ± 3.2 | 152.5 ± 2.9 (6 weeks) | 105.1 ± 3.2 | 116.3 ± 3.7 (6 weeks) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Shoulder FLEX (GNM, grades) mean ± SD | 105.1 ± 3.2 | 157.8 ±4.6 (6 weeks) | 104.7 ± 3.4 | 121.2 ± 15.7 (6 weeks) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Tendon thickness (USG, mm) mean ± SD | 6.4 ± 0.6 | 3.9 ± 0.3 (6 weeks) | 6.5 ± 0.6 | 5.2 ±0.4 (6 weeks) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Kamal et al. (2021) [37] | PI (VAS, cm) mean ± SD | 6.9 ± 0.6 | 1.7 ± 0.6 (6 weeks) | / | <0.01* | / | 6.9 ± 0.8 | 3.9 ± 0.7 (6 weeks) | / | <0.01* | / | <0.01* | ||||||||||||
| Shoulder ABD (GNM, grades) mean ± SD | 105.4 ± 3.3 | 153.5 ± 3.0 (6 weeks) | 105.3 ± 3.5 | 117.5 ± 3.9 (6 weeks) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Shoulder FLEX (GNM, grades) mean ± SD | 106.3 ± 3.2 | 157.9 ±4.6 (6 weeks) | 105.8 ± 3.7 | 123.2 ± 15.9 (6 weeks) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Tendon thickness (USG, mm) mean ± SD | 6.7 ± 0.7 | 4.0 ±0.4 (6 weeks) | 6.5 ± 0.7 | 5.4 ± 0.6 (6 weeks) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Sirbu et al. (2021) [38] | PI (VAS,cm) median(IQR) | 8(7-8.25) | 3(2-4) (3 weeks) | / | <0.01* | / | 8(8-9) | 4(3-6) (3 weeks) | / | <0.01* | / | 0.03* | ||||||||||||
| Function (CMS, score) mean ± SD | 26.3 ± 11.7 | 63.1 ± 18.1 (3 weeks) | 22.6 ± 9.9 | 54.0 ± 17.6 (3 weeks) | 0.09 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Disability (SPADI,%) mean ± SD | 67.9 ± 14.0 | 22.9 ± 16.8 (3 weeks) | 66.9 ± 12.5 | 33..3 ± 17.1 (3 weeks) | 0.04* | |||||||||||||||||||
| Aydin et al. (2021) [39] | Mean PPT (ALG, kg/cm2) mean ± SD | 50.3 ± 0.4 | 54.8 ± 0.4 (3 weeks) | / | <0.01* | / | 55.3 ± 0.4 | 54.7 ± 0.4 (3 weeks) | / | > 0.05 | / | <0.01* | ||||||||||||
| Shoulder FLEX (GNM, grades) mean ± SD | 110.3 ± 9.4 | 144.5 ± 8.2 (3 weeks) | 108.8 ± 8.4 | 141.8 ± 6.9 (3 weeks) | <0.01* | 0.10 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Shoulder EXT (GNM, grades) mean ± SD | 44.4 ± 2.7 | 59.6 ± 2.1 (3 weeks) | 44.1 ± 2.0 | 137.9 ± 1.8 (3 weeks) | 0.88 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Shoulder ABD (GNM, grades) mean ± SD | 107.9 ± 10.2 | 141.6 ± 9.4 (3 weeks) | 106.7 ± 9.2 | 137.9± 8.1 (3 weeks) | 0.15 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Shoulder IR (GNM,grades) mean ± SD | 53.7 ± 4.8 | 69.4 ± 4.7 (3 weeks) | 53.4 ±4.9 | 69.8 ±4.5 (3 weeks) | 0.80 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Shoulder ER (GNM,grades) mean ± SD | 54.6 ± 5.1 | 69.8 ± 4.1 (3 weeks) | 54.6 ± 5.1 | 69.9 ± 4.1 (3 weeks) | 0.89 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Elbow FLEX (GNM,grades) mean ± SD | 103.3 ±4.4 | 122.6 ± 3.6 (3 weeks) | 103.3 ±4.4 | 121.8±3.3 (3 weeks) | 0.84 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Disability (DASH,%) mean ± SD | 67.7 ± 4.4 | 38.7 ± 2.8 (3 weeks) | 67.7 ± 4.4 | 38.6 ± 3.1 (3 weeks) | 0.92 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Mean shoulder strength (DNM, lb) mean ± SD | 44.1 ± 2.2 | 46.9 ± 1.5 (3 weeks) | 37.1 ± 2.9 | 47.6 ± 1.4 (3 weeks) | 0.39 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Mean elbow strength (DNM, lb) mean ± SD | 48.0 ± 1.0 | 59.5 ± 1.7 (3 weeks) | 48.2 ± 0.9 | 59.6 ± 1.2 (3 weeks) | 0.55 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Dost and Eken (2021) [40] | PI (VAS, cm) mean ± SD | 6.4 ± 1.1 | 4.6 ± 2.0 (2 weeks) | 4.9 ± 1.3 (4 weeks) | / | <0.01* | <0.01* | / | 6.3 ± 1.1 | 4.0 ± 1.6 (2 weeks) | 3.7 ± 1.6 (4 weeks) | / | <0.01* | / | 0.24 | |||||||||
| PPT (ALG, kg/cm2) mean ± SD | 61.4 ± 22.2 | 59.1 ± 19.0 (2 weeks) | 56.8 ± 9.9 (4 weeks) | 0.52 | 0.26 | 65.1 ± 19.7 | 60.6 ± 12.3 (2 weeks) | 58.0 ± 6.9 (4 weeks) | 0.26 | 0.08 | 0.67 | |||||||||||||
| Disability (SPADI, score) mean ± SD | 64.4 ± 15.2 | 49.1 ± 16.9 (2 weeks) | 49.9 ± 13.6 (4 weeks) | <0.01* | <0.01* | 64.5 ± 13.5 | 40.0 ± 17.0 (2 weeks) | 38.6 ± 15.4 (4 weeks) | <0.01* | <0.05* | ||||||||||||||
| Zaki et al. (2022) [41] | PI difference (VAS) mean ± SD | NS | 3.4 ± 2.0 (2 weeks) | / | <0.01* | / | NS | 2.4 ± 1.3 (2 weeks) | / | <0.01* | / | <0.01* | ||||||||||||
| PI difference (SPADI, %) mean ± SD | 23.1 ± 9.6 (2 weeks) | 22.8 ± 18.1 (2 weeks) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Disability difference (SPADI, %) mean ± SD | 19.5 ± 16.6 (2 weeks) | 15.4 ± 14.9 (2 weeks) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yilmaz et al. (2022) [42] | PI (VAS, cm) mean ± SD | 6.6 ± 0.9 | 4.9 ± 0.8 (3 weeks) | 4.9 ± 0.8 (12 weeks) | / | <0.01* | <0.01* | / | 6.3 ± 0.6 | 5.1 ± 0.9 (3 weeks) | 5.5 ± 1.1 (12 weeks) | / | <0.01* | / | <0.01* | |||||||||
| PI at movement (VAS, cm) mean ± SD | 7.3 ± 0.7 | 5.2 ± 0.9 (3 weeks) | 5.0 ± 0.9 (12 weeks) | 6.8 ± 0.8 | 5.5 ± 1.1 (3 weeks) | 5.9 ± 1.2 (12 weeks) | ||||||||||||||||||
| PI at night (VAS, cm) mean ± SD | 6.9 ± 0.9 | 5.0 ± 0.8 (3 weeks) | 4.9 ± 0.8 (12 weeks) | 6.6 ± 0.9 | 5.4 ± 1.1 (3 weeks) | 5.8 ± 1.2 (12 weeks) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Shoulder FLEX (GNM, grades) mean ± SD | 152.8 ± 34.3 | 172.1 ± 21.5 (3 weeks) | 177.1 ± 11.7 (12 weeks) | 167.4 ± 19.8 | 174.5 ± 10.5 (3 weeks) | 177.0 ± 8.2 (12 weeks) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Shoulder ABD (GNM, grades) mean ± SD | 151.8 ± 34.4 | 172.8 ± 18 (3 weeks) | 176.5 ± 12 (12 weeks) | 160.9 ± 31.2 | 171.9 ± 15.3 (3 weeks) | 173.2 ± 14.9 (12 weeks) | 0.089 | |||||||||||||||||
| Shoulder IR (GNM, grades) mean ± SD | 78.1 ± 16.1 | 86.8 ± 7.2 (3 weeks) | 89.3 ± 3.5 (12 weeks) | 86.1 ± 10.2 | 88.3 ± 6.3 (3 weeks) | 88.3 ± 6.3 (12 weeks) | 0.102 | 0.102 | < 0.01* | |||||||||||||||
| Shoulder ER (GNM, grades) mean ± SD | 77.9 ± 15.2 | 86.8 ±7.2 (3 weeks) | 89.3 ± 3.5 (12 weeks) | 84.6 ± 12.5 | 88.3 ± 6.3 (3 weeks) | 88.3 ± 6.3 (12 weeks) | 0.06 | 0.06 | ||||||||||||||||
| Mean IR-PT (ISK DNM, grades/s) mean ± SD | 15.1 ± 10.5 | 20.4 ± 14.7 (3 weeks) | 21.4 ± 12.2 (12 weeks) | 11.9 ± 10.1 | 14.9 ± 13.8 (3 weeks) | 15.1 ± 13.8 (12 weeks) | <0.01* | |||||||||||||||||
| Mean ER-PT (ISK DNM, grades/s) mean ± SD | 7.5 ± 3.5 | 9.3 ± 5.6 (3 weeks) | 10.7 ± 7.5 (12 weeks) | 7.0 ± 3.2 | 7.0 ±3.0 (3 weeks) | 7.5 ± 5.2 (12 weeks) | 0.835 | 0.690 | ||||||||||||||||
| Function (CMS, score) mean ± SD | 57.2 ±9 | 75.3 ± 6.4 (3 weeks) | 75.8 ± 9.4 (12 weeks) | 63.1 ± 9.6 | 72.0 ± 9.5 (3 weeks) | 70.4 ± 8.9 (12 weeks) | <0.01* | |||||||||||||||||
| QoL (SF-36, score) | 41.6 ± 20.6 | 61.3 ± 13.5 | 63.7 ± 16 | 52.5 ± 19.9 | 58.6 ± 18.2 | 57.3 ± 19.4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Yeşilyaprak et al. (2023) [43] | PI (VAS, cm) mean ± SD | 5.6 ± 1.9 | 1.4 ± 1.0 (1 month) | / | <0.01* | / | without CG | N/A | ||||||||||||||||
| Active shoulder FLEX (GNM, grades) mean ± SD | 164.8 ± 10.2 | 175.7 ±3.7 (1 month) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Active shoulder ABD (GNM, grades) mean ± SD | 157.3 ± 25.0 | 174.2 ±7.9 (1 month) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Active shoulder IR (GNM, grades) mean ± SD | 65.1 ± 5.5 | 72.1 ±8.1 (1 month) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Active shoulder ER (GNM, grades) mean ± SD | 85.7 ± 4.5 | 89.0 ± 3.3 (1 month) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Passive shoulder FLEX (GNM, grades) mean ± SD | 167.1 ± 7.9 | 178.3 ±2.2 (1 month) | 0.002* | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Passive shoulder ABD (GNM, grades) mean ± SD | 160.1 ± 22.3 | 176.9 ±5.6 (1 month) | 0.001* | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Passive shoulder IR (GNM, grades) mean ± SD | 67.3 ± 6.1 | 75.0 ± 7.9 (1 month) | 0.006* | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Passive shoulder ER (GNM, grades) mean ± SD | 87.9 ± 3.0 | 89.7 ± 2.1 (1 month) | 0.050 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Function (CMS, score) mean ± SD | 57.9 ± 9.0 | 78.4 ±6.3 (1 month) | <0.01* | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Disability (SPADI, %) mean ± SD | 59.1 ± 16.0 | 25.7 ± 11.4 (1 month) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
[i] ABD – abduction, ALG – algometry, CG – control group, CMS – Constant-Murley Scale, DAHS – disabilities of the arm, DNM – dynamometry, ER-PT – external rotation peak torque, ER – external rotation, EXT – extension, FLEX – flexion, GNM – goniometry, HILT – high-intensity laser therapy, IQR – interquartile range, IR-PT – internal rotation peak torque, IR – internal rotation, NS – not specified, PI – pain intensity, PPT – pain pressure threshold, Q-DASH – quick disabilities of the arm, QoL – quality of life, SF-36 – short-form 36 health survey, SPADI – shoulder pain and disability index, SST – simple shoulder test, UCLA – University of California Los Angeles, USG – ultrasonography, VAS – visual analogue scale; * p < 0.05
Meta-analysis
Pain intensity
Ten studies were included in both the comprehensive meta-analysis and subgroup analyses to assess the effectiveness of HiLT compared to other treatment modalities regarding pain intensity. Pain intensity was measured using the VAS and SPAdi subscale. The pooled effect was determined utilising the random-effects model of derSimonian and Laird [28]. At the end of the treatment, both the VAS (Md = –1.36 cm; 95% Ci = –1.96, –0.75; p < 0.01) (Figure 3A) and the SPAdi subscale (Md = –4.9%; 95% Ci = –8.4, –1.4; p < 0.01, Figure 3B) showed a statistically significant reduction in pain intensity at rest in favour of HiLT. However, subgroup analyses revealed no significant differences when comparing HiLT versus placebo (Md = –0.24 cm; 95% Ci = –0.63, –0.16; p = 0.24) (Figure 3E), HiLT versus conventional physical therapy at one month (Md = –0.7 cm; 95% Ci = –2.5, 1.1; p = 0.05) (Figure 3C) and three-month follow-up (Md = –1.43 cm; 95% Ci = –3.13, –0.8; p = 0.28) (Figure 3d). The I2 coefficient derived from the analyses indicated a substantial level of heterogeneity across the studies, except for pain intensity measured using the SPAdi subscale and the comparison between HiLT and placebo, where heterogeneity was not statistically significant. The quality of evidence was deemed significant for pain intensity assessed with VAS but had low certainty, and it was not considered significant with a low level for the SPAdi subscale (Table 3).
Figure 3
Forest plots for pain intensity at rest (VAS) at the end of treatment (3A), pain intensity at rest (SPAdi, 3B), pain intensity at follow-up (1 month, 3C), pain intensity at follow-up (3 months, 3d) and HiLT versus placebo (3E)
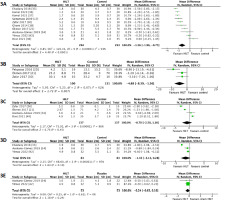
Table 3
Summary of findings and quality of evidence (GRAdE) for interesting outcomes
[i] Ci – confidence interval, CMS – Constant-Murley Scale, Md – mean difference, PT – physical therapy, SPAdi – Shoulder Pain and disability index, RCT – randomised controlled trial, VAS – visual analogue scale
[ii] a The high RoB was linked to the measurement of outcome data (57.7%) and bias due to deviations from the intended intervention (26%).
[iv] c Considering a direct comparison of interventions and outcomes relevant to the study, with applicability to the clinical context, it was found that the indirect evidence held little significance. d imprecision was assessed by examining the width of the confidence intervals (Cis) for the pooled Md, the crossing of the no-effect line in the meta-analysis, and the sample size (n < 200).
Shoulder ROM
A meta-analysis grouped data on shoulder RoM for abduction [20, 30, 31, 33, 36, 39, 42], flexion [20, 30, 31, 36, 37, 39, 42], external rotation [20, 30, 33, 39, 41], and internal rotation [30, 33, 39, 42]. The results revealed statistically significant changes in RoM for abduction (Md = 15.3°; 95% Ci = 4.4, 26.1; p < 0.01, Figure 4A) and shoulder flexion (Md = 12.8°; 95% Ci = 2.5, 23.1; p < 0.01, Figure 4B) after the treatment. However, no significant differences were observed between the groups in terms of external rotation movements (Md = 3.8°; 95% Ci = –5.1, 12.6; p = 0.4, Figure 4C) and internal rotation (Md = 2.9°; 95% Ci = –2.5,0.37; p = 0.29, Figure 4d) at the end of the treatment. All analyses exhibited a considerable I2 index [29]. The evaluation of the evidence suggests important changes for shoulder abduction and flexion, although with a low level of certainty (Table 3). For the other CRoMs, researchers assessed the evidence as not important due to the non-statistically significant changes [29].
Shoulder disability
The meta-analysis focused on shoulder disability (SPAdi), upper limb disability (dASH), and shoulder functionality (CMS). No statistically significant Mds were observed between the groups for SPAdi (Md = –4.4%; 95% Ci = –10.8, –1.9; p = 0.17, Figure 4E) and for dASH (Md = –5.9%; 95% Ci = –17.9, 6.0; p = 0.33). However, a significant difference was found for CMS (Md = 3.95 points; 95% Ci = 1.7, 6.2; p < 0.01). The I2 statistic was considerable for SPAdi and dASH but was not significant in terms of functionality evaluated by CMS [28]. Grounded in this outcome, the evidence pertaining to the effectiveness of HiLT in functioning with CMS is deemed not important and, with moderate certainty, was due to the RoB and inconsistency (Table 3) [27, 46].
Discussion
The application of HiLT in SAiS holds significant clinical importance, presenting a non-invasive therapeutic resource that has demonstrated efficacy in alleviating pain and enhancing mobility in many RCTs. The precise application of HiLT plays a crucial role in modulating the analgesic response and inducing muscle relaxation through thermal effects. Consequently, this therapeutic approach emerges as a valuable option for addressing SAiS, offering therapeutic benefits without the associated drawbacks of more invasive procedures or LLLT. in essence, HiLT provides a promising alternative for the management of this clinical condition.
This SR aimed to assess HiLT’s analgesic effects in SAiS patients compared to other physical therapies. The primary findings indicate potential effectiveness in reducing pain, improving functionality, and improving RoM in shoulder abduction and flexion. However, due to heterogeneity among RCTs and methodological issues, a cautious interpretation is necessary, influencing the overall recommendation based on the evidence.
HiLT and shoulder pain
This SR shows the effectiveness of HiLT in reducing pain among SAiS patients. HiLT exhibits a significant reduction of –1.4 cm (95% Ci: –2.0, –0.8) when compared to other treatments, including isolated exercise [30, 31, 33, 36, 37, 42], exercise combined with phonophoresis [37], ultrasound [17, 18, 30], thermotherapy [21], TENS [21], and HiLT placebo [34]. Notably, this pain reduction surpasses the CMid threshold (CMid = –1.4 cm) established for individuals with rotator cuff injuries [44]. Nonetheless, while clinically meaningful reductions in pain intensity were noted even at 1- and 3-month follow-ups, there were no statistically significant differences compared to conventional physical therapy interventions. This implies that HiLT is effective in the short and medium term, but other treatments may produce similar effects, albeit with a delay. These findings regarding HiLT’s effects on pain intensity with VAS align with prior research on LLLT in shoulder tendinopathies. These studies have found that laser therapy reduces pain by –1.3 cm (95% Ci: –1.7 to –2.4) and –2.4 cm (95% Ci: –1.3 to –2.8) compared to other physical or exercise therapy methods and sham LLLT, respectively [11]. This suggests similar analgesic effects and supports the idea that these lasers share a common physical mechanism of action. However, more research is needed to directly compare the effectiveness of HiLT and LLLT, as no study in the review conducted such a comparison. These findings endorse laser therapy’s efficacy in alleviating shoulder pain, resulting in an important GRAdE rating despite some uncertainty due to bias and variability. Currently, HiLT is regarded as a clinically equivalent alternative to LLLT, making the choice between these approaches contingent on resource availability, cost considerations, or individual patient preferences.
The VAS outcomes align with those from the SPAdi sub-scale, where HiLT exhibits a greater pain reduction compared to the control treatment, with a difference of –5.0% (95% Ci: –8.4, –1.39). it’s worth noting that this difference falls below the CMid threshold of 14 to 20% that is established for the SPAdi [45]. it should be considered that only three studies utilised the SPAdi subscale [20, 21, 30], rendering the VAS results more reliable. Notably, no significant discrepancies in pain intensity at treatment completion emerged in the HiLT versus placebo comparison. Notably, this analysis hinged on just two studies [34, 42], highlighting the need for more extensive research for definitive outcomes. in patients with SAiS, an important clinical metric is the Patient Acceptable Symptom Status (PASS) Assessment, which employs VAS scores to identify the highest symptom level deemed acceptable by patients. An average PASS of 3 cm has been established as acceptable (95% Ci: 2.3, 3.7). While not directly assessed in the referenced RCTs, the pain intensity at the end of treatment aligns with the acceptable PASS for several RCTs [17, 18, 30, 31, 37]. in SAiS rehabilitation, exercise integration is crucial due to the central role of muscle weakness [46, 47]. Several RCTs in this study integrated exercises within HiLT protocols. Given that there is a strong link between SAiS and rotator cuff and postural muscle weakness, physical therapy is very important for three very important reasons: managing symptoms (using HiLT or other methods), strengthening muscles, and postural re-education [46].
HiLT and RoM
The results show that HiLT is better than traditional physical therapy at increasing the RoM of the shoulder in flexion and abduction by an average of 15.3° (95% Ci: 4.4–26.1) and 12.9° (95% Ci: 2.5–23.1), respectively. These improvements are greater than the minimal detectable change (MdC), which is 8° for flexion and 4° for abduction [48], and align with the MCid reported, ranging from 11° to 16° [49]. increased shoulder flexion and abduction influence scapular plane arm lifting, which is limited in SAiS patients [1, 5]. This movement improves movement patterns, strengthens the rotator cuff, and prevents injuries [50].
The thermal and analgesic benefits of HiLT increase RoM. Heating the tissues relaxes muscles and interrupts the cycle of painful muscle spasms [51, 52]. At the same time, pain reduction diminishes abnormal afferent information that affects movement performance [53]. Since it was applied directly to the deltoid, which controls abduction and flexion, the HiLT likely had a greater effect on RoM. importantly, focused HiLT administration to specific rotator muscles may improve shoulder rotation. The limited number of RCTs on the rotation RoM may make it difficult to draw conclusions.
Although HiLT can enhance movement, it is recommended to combine it with more targeted interventions, such as exercises or manual therapy, for optimal results [54].
HiLT and disability
According to SPAdi and CMS, HiLT is effective in reducing disability by –6.6% (95% Ci: –12.5, –0.6) and enhancing functionality by 4 points (95% Ci: 1.7, 6.2), respectively. in patients with rotator cuff injuries, the SPAdi values for disability are lower than the MCid (8 to 13 points, or 10 to 16%), while the CMS values for functionality are concordant with the MCid (2 to 16 points) [55, 56]. disability has gained increasing importance in clinical trials. This outcome is crucial, as treatments should not only evaluate the influence of symptoms on functionality, a relevant aspect for patients [57]. Although HiLT is primarily intended to alleviate pain, its secondary effect on disability is significant, as pain frequently induces a dread of moving that restricts functionality. Furthermore, this dread of movement frequently contributes to the condition’s chronicity [58–60].
Recommendations
This review emphasises the variability of parameters in the use of HiLT in studies, which makes establishing a standard dose challenging. Nevertheless, a dosage based on common parameters is proposed: wavelength 1064 nm, average power 8–12 W, total energy 3050 J for three phases (1000 J, 50 J, and 2000 J), continuous mode for phases 1 and 3, pulsed mode for phase 2, scanning application on the deltoid (phases 1 and 3), and punctual on pain spots (phase 2).
Furthermore, the number of sessions should range between 12 to 15 over the course of four weeks. To improve treatment outcomes, it is suggested that resistance and postural exercises be added to HiLT [46, 47, 54]. in addition, the literature suggests investigating approaches that incorporate the neuroscience of pain, motor imagery techniques, and behavioural modification, especially in chronic pain [46].
Limitations
This SR underscores its commitment to transparency, aligning with the rigorous PRiSMA guidelines and ensuring the registration of the protocol in PRoSPERo. However, it is imperative to recognise certain inherent limitations.
(1) The inability to exclude articles in languages other than English and Spanish represents a notable constraint, given the multinational origin of randomised controlled trials (RCTs), spanning countries like Turkey, iran, india, and Taiwan. The potential existence of pertinent articles in other languages, particularly within the ‘grey literature’, introduces a degree of limitation [61]. Similarly, efforts should be directed towards mitigating this issue, considering the use of eight search sources, with some encompassing grey literature, notably Google Scholar.
(2) Confronting substantial heterogeneity among the included studies has rendered the formulation of more conclusive findings regarding the evidentiary support for HiLT addressing pain, RoM, and disability a complex task.
(3) Methodological limitations, including challenges related to bias due to deviations from the intended intervention or measurement of the outcome data, observed in certain RCTs warrant acknowledgement, as these aspects may exert an influence on the robustness and interpretability of the reported results.
Conclusions
This review supports the efficacy of HiLT in reducing pain in patients with SAiS. Significant improvements in shoulder flexion and abduction are observed, as well as a decrease in associated disability. These results are consistent with previous reviews on LLLT, supporting the validity of both treatment options. However, additional comparative studies are needed for a more precise evaluation of the effectiveness of both types of therapeutic lasers.
The authors highlighted the importance of evidence, but methodological inconsistencies in some RCTs affecting the certainty of results must be considered.