Introduction
Sexual function is important for physical, psychosocial and emotional well-being and serves as a marker for overall general health [1]. Sexual dysfunction can have a huge impact on the overall sexual health of an individual and refers to a problem that occurs during the sexual response cycle that prevents the individual from experiencing satisfaction from sexual activity [2]. A proportion of men and women experience varying levels of sexual dysfunction worldwide, and studies have shown that the prevalence is increasing [3]. Given that it affects a sizable portion of men globally and has a substantial influence on quality of life and mental health, male sexual dysfunction is a condition of public health importance. Male sexual function is a complex biopsychosocial process that can be affected by endocrine, neurological, psychological, vascular, interpersonal, and sociocultural factors [4].
Male sexual dysfunction (MSD) can be classified into low libido, erectile dysfunction, Peyronie’s disease, ejaculatory and orgasmic disorders [5]. It is estimated that one-third of men will experience one form of sexual dysfunction at one point in their lives. Ejaculatory disorders can be further classified into premature ejaculation, delayed ejaculation, anejaculation, and retrograde ejaculation [6]. Erectile dysfunction (ED) and premature ejaculation (PE) are the most common sexual disorders in men [7]. Data from the European Male Ageing Study [8] revealed that 6% of men reported experiencing severe orgasmic impairment and 30% having erectile dysfunction (ED), both of which were strongly correlated with advanced age and concomitant morbidities. Also, the PE Prevalence and Attitudes Survey [4], which engaged more than 12,000 participants, recorded a 22.7% PE prevalence within a period of 24 years.
Male sexual dysfunction can be treated with physiotherapy interventions, especially in cases of erectile dysfunction, premature ejaculation, and pelvic pain syndrome [9–11]. Through a variety of methods, including pelvic floor muscle exercises, biofeedback, and electrical stimulation, physiotherapists can assist in improving blood flow to the penis in the case of erectile dysfunction [12]. Exercises targeting the pelvic floor muscles in particular have been proven to help men with ED improve their erectile function [12]. In cases of premature ejaculation (PE), physiotherapy interventions such as strengthening the pelvic floor muscles, which can enhance ejaculatory control, have been shown to effectively manage this condition. Furthermore, methods like deep breathing exercises and relaxation exercises might be helpful in controlling PE [12].
It is sacrosanct that physiotherapy management should always be administered by qualified and licensed physiotherapists, especially since there is a need to adopt strict ethical protocols because of the sensitivity of interventions for the reproductive organs. Previous studies have focused more on the role of physiotherapy in the management of male sexual dysfunction [12–14]. However, it is necessary to document the knowledge, attitude, and practice of physiotherapists towards male sexual dysfunction, which has not been investigated to the best of the researchers’ knowledge. When this information is investigated, it may contribute to the diagnosis and treatment of patients with MSD by physiotherapists, thereby fostering an improvement in the quality-of-care outcomes for patients with MSD. For the researcher, information on the KAP of physiotherapists regarding MSD may be a measure of knowledge translation activity in physiotherapy practice.
Subjects and methods
The study utilised a cross-sectional survey design. A purposive sampling technique was used in recruiting participants for the study. Participants were invited to participate in the research via the professional/workgroup’s WhatsApp communications programme. Informed consent and a cover letter were delivered alongside the questionnaire link via this means. Participants included physiotherapists with at least 2 years of post-graduation experience working in a teaching hospital in South-West, Nigeria, and physiotherapists who may have been involved in the management of male sexual dysfunction. The study lasted three months, with the selected tertiary hospitals as the setting of the research. Those who did not meet these criteria were excluded from the study. The total sample size was determined using the formula:
n = (Z2p(1–p)}/e2}÷{1+(Z2p(1–p)/e2N)} [15],
where the confidence level = 95%, proportion (p) = 0.5, error (margin) (e) = 0.05, Z-score = 1.959964, and the total number of registered physiotherapists practicing in a teaching hospital in south-western Nigeria (N) = 124. The minimum sample size for this study was calculated to be 74. Eventually, 75 physiotherapists were recruited for the study.
A self-developed questionnaire was used to obtain information on the knowledge, attitude, and practice of physiotherapists towards male sexual dysfunction. The questionnaire contained four sections, including: Section A, which sought to elicit demographic data in a closed multiple-choice format (six questions). Section B consisted of eleven questions, which assessed the knowledge of physiotherapists towards male sexual dysfunction. This section had three options: Yes, No, and Uncertain. Section C had ten questions on a five-point Likert scale (strongly agree, agree, neutral, disagree, strongly disagree) that assessed the attitude of the physiotherapist towards the management of MSD. Section D had ten questions on the practice of physiotherapists towards the management of MSD, with options of yes, no, and uncertain. For the knowledge and practice questions, the right answer (yes) was allotted a score of one while a zero score was allotted to the ‘no’ and ‘uncertain’ options, resulting in maximum scores of 11 and 10, respectively. For the attitude questions, ‘strongly agree’ and ‘agree’ were allotted scores of two and one, respectively. A score of zero was allotted to ‘neutral’, ‘disagree’, and ‘strongly disagree’, resulting in a maximum score of 20. The negatively worded questions were recoded during scoring. The higher the score, the better the knowledge, attitude and practice. The median scores were used to dichotomise the responses into good and poor knowledge, attitude and practice (KAP).
The surveys were delivered to the study participants through Google® Forms. Prior to the main survey, a pilot study was carried out in order to evaluate the self-developed questionnaire’s internal consistency, face validity, and intra-rater test-retest reliability. The intra-rater test-retest reliability involving 15 therapists was determined for the developed questionnaire. This had an item-by-item kappa value of 1 for all 31 items correlated, implying excellent item-by-item internal consistency. The initial intraclass coefficient (ICC) for the research instrument was 0.601 with a 95% confidence interval of 0.412–0.718. The item-by-item Cronbach’s alphas were used to improve the ICC by removing some redundant questions. This resulted in a new ICC of 0.775 with a 95% confidence interval of 0.69–0.85. An expert panel of four physiotherapists conducted a face validity check on the questionnaire. Two physiotherapists had PhD degrees in physiotherapy, one had a master’s degree in physiotherapy and the other had a bachelor’s degree in physiotherapy. This reduced the threats to validity by improving the data collection tool and ensuring that it measured what it purported to measure.
Data analysis
A test of normality was performed on the knowledge, attitude and practice scores using the Shapiro–Wilk test with a p-value of < 0.0001 for the knowledge score, 0.023 for the attitude score, and < 0.0001 for the practice score, showing that the data is not normally distributed. Descriptive statistics of mean, median, standard deviation (SD) and interquartile range (IQR), frequency distribution, and percentage were used to summarise the participants’ demographic data and also their knowledge, attitude and practice related to the management of male sexual dysfunction. Inferential statistics of Spearman’s correlation were used to determine the association between the demographic variables and each of the knowledge, attitude, and practice variables. The Mann–Whitney and Kruskal–Wallis tests were used to assess the median differences of KAP across the sociodemographic variables. Chi-square and logistic regression analyses were also performed. The level of significance was set at p < 0.05. The Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) version 25.0 was used to analyse the data.
Results
A total of 75 physiotherapists responded to the study. The mean age of the participants was 34.51 ± 8.93 (range: 21–60) years, with a mean year of experience of 8.39 ± 7.26 (range: 1–31) years. Respondents comprised 57.3% (n = 43) men; 56.7% (n = 44) reported a bachelor’s degree as their highest level of qualification, and many (28.0%, n = 21) of the respondents specialised in neurology physiotherapy. A total of 25.0% (n = 15) of the respondents worked at Lagos University Teaching Hospital, Idi-Araba, Lagos State. Other demographic characteristics of the respondents are detailed in Table 1.
Table 1
Sociodemographic characteristics of the respondents
The response distributions on KAP about MSD are presented in Appendices 1–3.
The knowledge score ranged from 2 to 10, with a median knowledge score (IQR) of 8 (7–8). A total of 97.3% (n = 73) of the respondents have heard of male sexual dysfunction, and 78.7% (n = 59) of the respondents could manage a patient with male sexual dysfunction. Furthermore, 92.0% (n = 69) of the respondents agreed that erectile dysfunction is a type of MSD, and 50.7% (n = 38) agreed that premature ejaculation is the most common type of MSD. More than half (52%) of the participants declared having good knowledge (Figure 1).
The attitude score ranged from 0 to 18, with a median attitude score (IQR) of 11 (8–15). It was observed that a large percentage of the respondents agreed or strongly agreed with all the questions. More than half (53.3%) of the participants declared having good knowledge (Figure 1). The practice score ranged from 0 to 10, with a median practice score (IQR) of 9 (7–10). It was observed that the majority of the respondents had a high practice score and 60% declared having good practice (Figure 1).
Figure 1
Knowledge, attitude and practice of respondents on the management of male sexual dysfunction
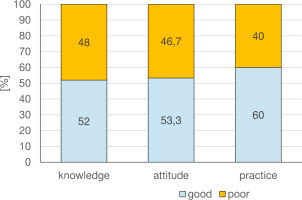
Table 2 shows a comparison of the participants’ KAP across sociodemographic characteristics. There was no significant gender difference in knowledge (p = 0.441), knowledge across participants’ level of qualification (p = 0.244), knowledge across area of specialisation (p = 0.253), or knowledge across place of work (p = 0.571). There was no significant gender difference in the attitude components (p = 0.405), attitude across participants’ areas of specialisation (p = 0.145), or attitude across place of work (p = 0.259). Participants with a higher level of qualification had a significantly higher attitude score (p = 0.022) towards the management of male sexual dysfunction. There was no significant gender difference in the practice components (p = 0.310), practice across the participants’ level of qualification (p = 0.098), practice across area of specialisation (p = 0.655), or practice across place of work (p = 0.637).
Spearman’s correlation coefficient revealed a weak positive and significant relationships between age and each of knowledge, attitude and practice, while years of experience demonstrated weak significant correlations with both attitude and practice. Chi-square showed a significant association between knowledge and years of experience, while specialisation was significantly associated with attitude (Table 3). Gender, age, education, and place of work were not significantly associated with KAP (p > 0.05).
Table 4 presents a logistic regression analysis of the factors that predict the knowledge, attitude and practice towards the management of MSD. When factors such as age, gender, years of experience, education, specialisation and place of work were entered, only age and specialisation were significant. With a unit increase in age, there is a concomitant increase in knowledge (OR = 1.152, CI = 1.001–1.326, p = 0.049). Physiotherapists with the paediatrics specialisation were 90.9% less likely to demonstrate a positive attitude towards the management of MSD in comparison with the neurology specialisation (OR = 0.091, CI = 0.016–0.500, p = 0.006).
Discussion
The study assessed the knowledge, attitude, and practice of physiotherapists towards the management of male sexual dysfunction in selected teaching hospitals in SouthWest, Nigeria. The findings of this study showed that the majority of the participants had a good knowledge of what male sexual dysfunction is, and most participants reported that they could manage a patient with male sexual dysfunction. The relatively good knowledge of physiotherapists about the management of MSD may stem from the extent of exposure to the management of this condition, as clinicians from tertiary health institutions are often said to be more exposed to a wide range of ailments of public health concerns. Tang et al. [16] reported a knowledge gap about sexual dysfunction among Chinese urologists and andrologists. The present study reports good knowledge among our study population (physiotherapists); however, the differences in knowledge between our research and that of Tang et al. [16] may not be immediately understood. A good number of the participants had a positive attitude towards the management of male sexual dysfunction. Patients with sexual dysfunction are prone to psychosocial stress, so the clinician will need to display a positive attitude and has to prompt the co-operation of the patients [17]. A sizeable number of participants reported that they enjoy managing a patient with male sexual dysfunction, while a few participants are comfortable talking to male patients about their sex lives. There may be some reasons behind this, such as improving health literacy among the physiotherapists and gender dynamics [12].
Table 2
Comparison of knowledge, attitude and practice scores across sociodemographic variables
Table 3
Relationship between age, years of experience, specialisation, knowledge, attitude, and practice of participants towards the management of male sexual dysfunction
Table 4
Predictors of knowledge, attitude and practice
The majority of the participants know the influence physical health has on sexual functioning, and they are proactive in integrating the knowledge they have into the therapeutic approach of addressing a patient with male sexual dysfunction. This may be because the participants understand that the musculoskeletal system, neurological pathways, and vascular systems play an important role in male sexual functioning [13]. Some of the participants incorporate sexual function assessment as part of their management. Most of the participants employ a variety of physiotherapy techniques, such as pelvic floor exercises, biofeedback, etc., to manage a patient with male sexual dysfunction. This may be because the techniques are evidence-informed and well documented in the relevant literature [13, 14].
The level of education was significantly associated with a more positive attitude of physiotherapists towards the management of male sexual dysfunction. Increasing the knowledge base of healthcare professionals has significantly proven to have the biggest positive influence on the quality of care, especially the attitude of healthcare professionals [18–20]. It is often observed that when healthcare professionals acquire further educational training, it improves their knowledge, attitudes and practices. Our data also suggest a better attitude and practice with increased years of experience. It is assumed that with increased years of experience, the participants will have been exposed to more cases and thus improved their attitude and practice.
This study showed that the age of physiotherapists plays a significant role in the management of male sexual dysfunction. This was buttressed by the regression analysis. For example, an older physiotherapist might have more clinical experience, which can affect the way they approach the management of a patient with MSD. Also, older physiotherapists who have seen positive outcomes in their treatment over the years may have a more confident and structured approach to managing a patient with MSD.
One of the significant findings of the present study is that the specialisation of the physiotherapists influences their attitude towards the management of MSD. Those in the neurology specialisation demonstrated significant positive attitudes towards the management of MSD. Although MSD is caused by neurologic, neurovascular, vasculogenic and hormonal factors as well as psychosocial problems, the incidence of MSD is predominantly high among neurologic patients [21–24]. Thus, physiotherapists with the neurology specialisation may be exposed to more cases of MSD, and this may improve their attitude over time. Our data suggests this observation, as those in the paediatrics specialisation were 90.9% less likely to demonstrate a positive attitude compared to the neurology specialisation. Male sexual dysfunction is not a wellbeing concern that is relevant in the paediatric population, which explains why physiotherapists in this sub-population demonstrate a less positive attitude towards the management of MSD.
Limitations
This study has some limitations that must be considered while interpreting the results. First, we used a self-developed questionnaire that had closed-ended options without giving the physiotherapist the opportunity to give an experience-driven response. A mixed-methods approach is recommended in future research to deal with this limitation. Lastly, our methodology is prone to recall bias, and the information reported by the physiotherapist may be limited by the quality of the physiotherapist’s memory. However, we believe that the management of MSD is a unique challenge, and most physiotherapists should vividly recall such experiences. Despite these limitations, the study provides an accurate report of KAP of physiotherapists in the management of MSD.
Conclusions
Based on the study’s findings, it can be concluded that the physiotherapists in this study exhibit good knowledge, a positive outlook, and efficient procedures for treating male sexual dysfunction. These qualities were significantly predominant among the older physiotherapists who reported positive attitudes among the neuro-physiotherapists. The implication of this is that there is a need for more training for all physiotherapists within other subspecialties to hone their competencies in the management of male sexual dysfunction. The researchers recommend targeted continuous professional development to improve the knowledge and practice of physiotherapists to improve the quality of care rendered by physiotherapists to men with sexual dysfunction. This study therefore emphasises the significance of ongoing professional development while highlighting the potential advantages of focused educational interventions for physiotherapists at various points in their careers and re-echoing the obvious fact that competency in practice is expected to improve as duration of practice increases.

